What is a Bond: Definition, Guide and Examples
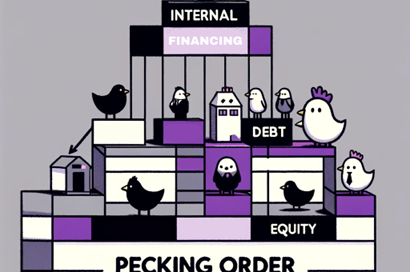
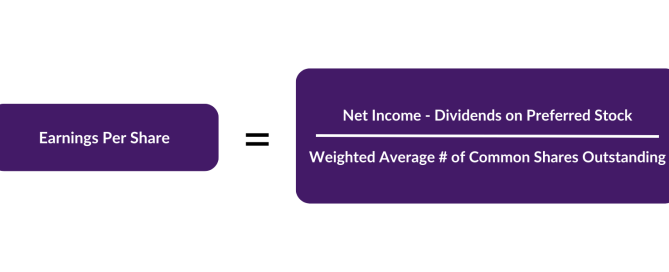
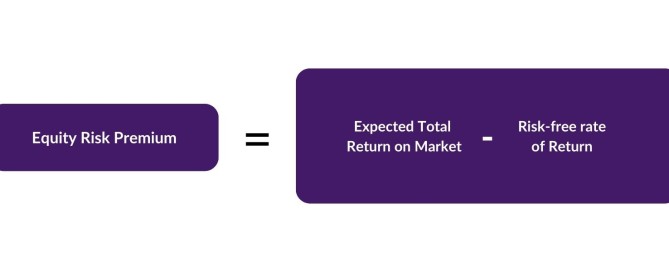
What is a Bond: Definition, Guide and Examples Bonds represent one of the cornerstone investment vehicles in global capital markets, playing a crucial role for fund raising for organisations and presenting investment opportunities for institutional and retail investors. The vast majority of bonds are fixed-income securities and have therefore bonds have historically provided investors